EIFS or Synthetic Stucco Inspections
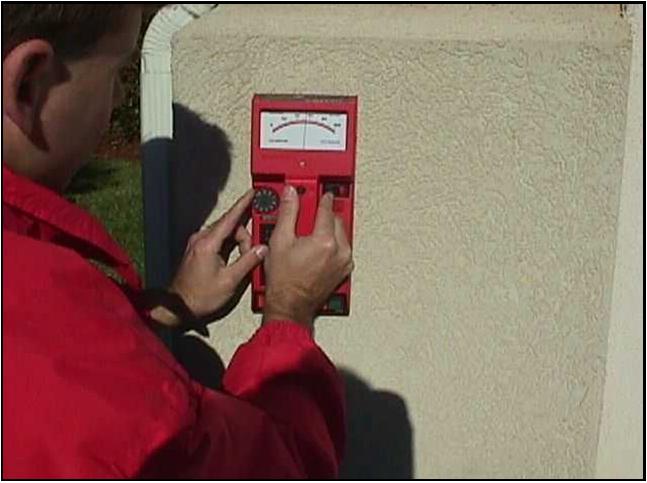
To probe for a moisture reading, the inspector will first drive two steel pins through the EIFS into the wall. The inspector should note whether the substrate or framing seems firm or soft, keeping in mind that different substrates may be used on the home. The pins are withdrawn, and then replaced with the Teflon-coated probes of the Delmhorst meter. The readings are recorded and we note the “feel” of the framing or substrate wood. The small inspection holes are sealed with an appropriate sealant, preferably matching the color of the EIFS as closely as possible.
View A Sample Inspection Report
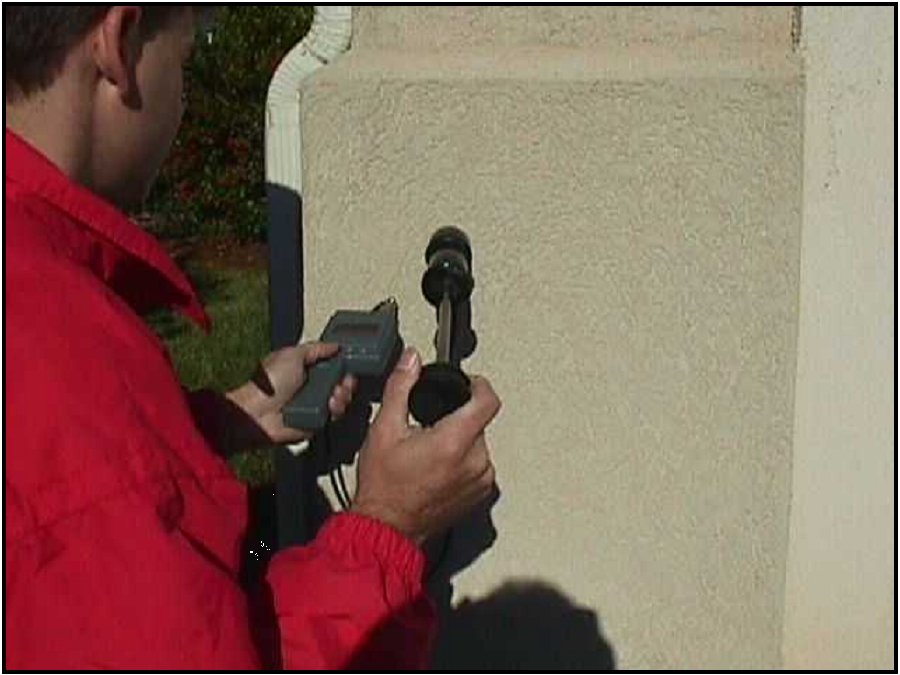

Delmhorst Moisture Probe Meter

Tramex Wet Wall Detector
Watch this 2 minute video to see how hardcoat stucco probe testing is performed on the exterior of a stucco property.
Hard Coat or Traditional Stucco Inspections
We use the following inspection protocol for qualifying a hardcoat stucco homes.
We first, determine the type (1 coat or 3 coat) system on the home and identify the substrate.
Test three (2) locations below every kickout location (whether flashing is installed or not)
- Directly below the kickout (6” to 12”)
- Joist band at closest floor line.
- Show close-up photographs of the flashing or if it is missing.
Under double-hung or single-hung windows, probe windows directly below one of the miter joints and/or mullions. Also, probe test and document all windows that are showing signs of possible moisture intrusion and/or wood rot. Note on the report whether the area probed “feels” firm or soft when probed. If the substrate is soft (ie. deteriorated), map the damaged area and test the rim joist for damage.
Under all casement, custom, oversized or fixed placement windows, probe under each miter joint and/or mullion joints. Keep in mind that fixed placement windows sometimes have glazing failures that allow moisture intrusion along the entire length of the window and not just at the miters.








Recent Comments